JiaoGulan Aum MiracleTea gift pack (30g)
€11.11
Limited Supplies – Available in Eu
Jiaogulan is a herb from my native southern China that I believe possesses the most wide-ranging benefits for human health and wellness of any plant yet discovered.
This may seem like a bold statement, but having studied this remarkable tonic herb for more than twenty years, I can assure you that there is strong scientific support to back up my passion for jiaogulan – Dr. Jialiu Liu, ‘Father of Jiaogulan’
Available on backorder
Description
What is Jiaogulan?
Jiaogulan is a herb from my native southern China that I believe possesses the most wide-ranging benefits for human health and wellness of any plant yet discovered. This may seem like a bold statement, but having studied this remarkable tonic herb for more than twenty years, I can assure you that there is strong scientific support to back up my passion for jiaogulan.Dr. Jialiu Liu, ‘Father of Jiaogulan’
“After many years studying hundreds of herbs, we ultimately came to the realization that Jiaogulan was not only the rainforest’s most precious gift, but was in fact nature’s greatest treasure. We began to use Jiaogulan in our medical university hospital with great success for a wide variety of conditions, and before long, it was also being used at numerous other hospitals throughout China.”Dr. Jialiu Liu, ‘Father of Jiaogulan’
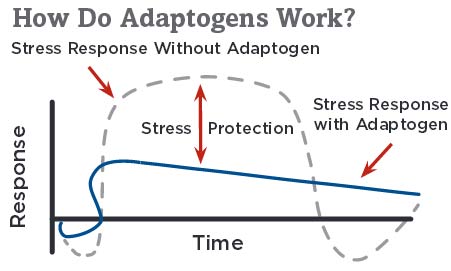
Jiaogulan the Adaptogen
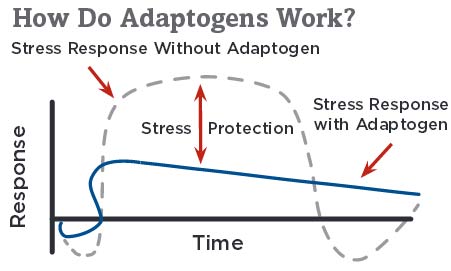
For a plant to be qualified as an adaptogen, it must meet the following 3 criteria as defined by Israel I. Berkhman, PhD, and Dr. I. V. Dardymov in 1968:
- Nontoxic
An adaptogen is nontoxic to the recipient. It must cause minimal side effects on physical or mental health.
- Increases Resistance to Stress
An adaptogen produces a nonspecific response in the body—an increase in the power of resistance against multiple stressors including physical, chemical, or biological agents in multiple nonspecific ways, including the building of a reserve of “adaptive energy”. This reserve is then used when an actual stressor arises, instead of depleting the cells of vital energy.
- Has a Normalizing Effect
An adaptogen is “intelligent” in that it has a normalizing influence on physiology, regardless of the direction of change from the normal state caused by the stressor. This normalizing influence implies the capability of adaptogens for a bidirectional effect on physiological function. They are capable of either toning down or strengthening the activity of multiple systems, including the neuro-endocrine and immune systems, depending on the need. For example, if a person with high blood pressure is given Jiaogulan, their blood pressure will drop. If on the other hand their blood pressure is below normal, it will raise.
Some of these triterpenoid saponins have been identified as having adaptogenic properties, while others were found to have anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective (protecting the liver), adrenal gland strengthening, and immune system modulating effects.2
Jiaogulan is a premier adaptogen, and has been described as “Like Ginseng, but better than Ginseng” because of the energizing effect both plants have on the body.
However, while Ginseng is often poorly tolerated and can cause insomnia, tachycardia and nervousness, Jiaogulan has the opposite effects because it is a superior adaptogen.
Jiaogulan the Supreme Antioxidant
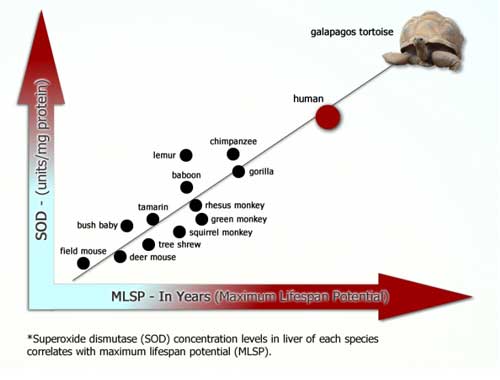
Jiaogulan contains some of the rarest and most powerful antioxidant properties.It stimulates the body’s own production of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Glutathione, and Catalase, the 3 most important endogenous (produced by the organism) antioxidants that help your body fight against free radicals – the cause of aging and a myriad of diseases.
For years, scientists have sought ways to boost the body’s most powerful internal antioxidants: Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and Glutathione.
Until now, no natural and effective ways of boosting SOD levels had been discovered.
Glutathione is the other vitally important endogenous antioxidant, produced within each and every cell of your body. It prevents cell damage by neutralizing free radicals and maintains dietary antioxidants such as vitamins C and E in their active forms so that they can keep fighting free radicals.
It also plays a critical and integral part in detoxifying the body by binding to pesticides, heavy metals and other toxins until they are excreted, it regulates protein and DNA synthesis and cell growth, and is critical in helping your immune system perform its role of fighting infections and preventing cancer.
Lastly, glutathione helps us reach peak mental and physical function by decreasing muscle damage, reducing recovery time, increasing strength and endurance, and shifting metabolism from fat production to muscle development.
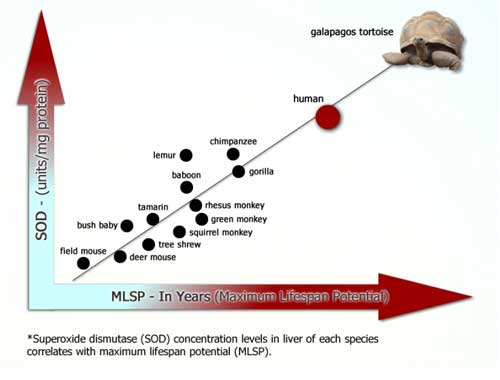
Cutler’s cross-species investigations strongly suggest that SOD is a primary determinant of longevity in mammals, and that increased SOD production plays a key role in the higher order of mammals’ evolution from shorter to longer life spans.
Jiaogulan Promotes Youth and Longevity by Stimulating SOD and Glutathione Production
Jiaogulan’s remarkable ability to stimulate the body’s own production of both SOD and glutathione must be at the heart of the reason why it has been so strongly associated with anti-aging and longevity.Science has finally found the mechanism to explain how and why so many Jiaogulan users in China lived to be 100 years old in good health, and why they called it “The Herb of Immortality”.
The stimulation of SOD and glutathione production may also be greatly responsible for the preventive and therapeutic qualities the herb has.
The older you are the better!!
A Guiyang Medical College human clinical trial with 610 healthy middle and advanced age patients, aged 50 to 90, showed that SOD levels returned to their youthful levels after only one month of daily intake of 20 mg of gypenosides (the main active ingredients in Jiaogulan)!
Those between 70 and 90 years of age saw an average decrease in the harmful superoxide and other radicals of 21.4% and an average increase in internally produced SOD of 282.8%, while in the 50 to 69 age group there was a 15.6% decrease in oxidant levels and a 116.1% increase in SOD concentrations! A control group not receiving gypenosides from Jiaogulan did not experience any change.22
In another 2-month double-blind experiment at the Shanghai Institute of Geriatrics, 51 elderly patients were administered 60mg of Jiaogulan gypenosides daily for 2 months, while a control group of 40 patients were given a placebo. This study too found a significant increase in SOD levels and significant decrease in cell damage from oxidation. In addition, the researchers saw an improvement in the memory of the patients. None of these effects were observed in the placebo group.25
In addition to these landmark human studies, there have been many animal and in-vitro studies that have demonstrated the protective effects Jiaogulan has on the body’s cardiovascular21, 26, 27, 28, 29, 31, immune26, 32, nervous31, 33, 34, 35 36,37, 38, 49, and reproductive39 systems and various organs, such as the liver26, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, kidneys29, 31, stomach46, and skin47, 48, due to its ability to boost the organism’s own defenses against free radicals by stimulating the production of SOD, Glutathione 31, 35, 37, 43, 44, 50, 51, 52, and Catalase44, 48, 50, 51.
This boost of endogenous antioxidants was also found to have anti-inflammatory29, 53, anti-cancer 53, 54 and anti-aging 32, 47, 48, 55, 56 effects, and to be beneficial for athletic performance and faster recovery from exercise51.
Jiaogulan as a Nitric Oxide Regulator
Nitric Oxide (NO) is a gas and free radical produced in the body that is deemed so important in human physiology that it was named “Molecule of the Year” by the journal Science in 1992.58Few people realize it, but Nitric Oxide is probably the most important chemical compound for cardiovascular health.
The President of the American Heart Association called it “the most important discovery in the history of cardiovascular medicine”, and in 1998, the Nobel Prize for Medicine was given to the three scientists who discovered the role of Nitric Oxide as a cardiovascular signalling molecule.
Simply put, adequate Nitric Oxide production is the first step in a chain reaction that promotes healthy cardiovascular function, while insufficient production triggers a cascade of destruction that eventually results in heart disease.
However, Nitric Oxide concentrations that are too low or too high can result in a number of serious conditions and diseases like heart disease, stroke, cognitive decline, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and many more.
Studies have now shown that Jiaogulan has the remarkable ability to both protect and stimulate the production of Nitric Oxide (NO) when your body produces too little of it6, 57, 59, 60, 61, or to limit its production when it is out of control38, 62, 63, 64.
Since diseases arise when Nitric Oxide levels are either too high or too low, the regulatory effect of Jiaogulan on its production is crucial in maintaining good health through balance, and is further testament to the herb’s adaptogenic properties.
Jiaogulan Promotes Cardiovascular Health
Heart and blood vessel disease is the #1 cause of death in the world, resulting in 17.3 million annual deaths globally. In the United States it killed almost 800,000 people in 2013 alone.The majority of problems classified under the umbrella of heart disease are related to a process called atherosclerosis, or thickening and hardening of the arteries.
Jiaogulan prevents damage to the arterial lining in two ways:
First, it neutralizes the oxidative damage to the arteries caused by free radicals and cholesterol through its powerful antioxidant effects26, 27, 29 (see Antioxidant section).
The second way Gynostemma prevents endothelial damage is through its ability to regulate blood pressure, either lowering it 63, 65 or elevating it 63 depending on the need.
The herb’s ability to lower blood pressure is at least in part due to its protection and stimulation of endothelial Nitric Oxide production.6, 57, 59, 60
One double blind clinical study of patients with high blood pressure showed that Jiaogulan is almost as effective as Indapamide (a high blood pressure drug), and almost twice as effective as Panax Ginseng (82%, 93%, and 46% respectively) in reducing high blood pressure.65
Jiaogulan has demonstrated its ability to lower bad cholesterol (LDL) and triglyceride levels, while raising good cholesterol (HDL) levels in a number of studies.18, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84
It achieves this by improving the body’s ability to metabolize fat and by stimulating Nitric Oxide production, which suppresses the damage done to bad (LDL) cholesterol by free radicals.
Jiaogulan Prevents Platelet Stickiness and Blood Clots
Plaques grow over years and slowly blocks blood flow in the arteries. What’s worse, cholesterol plaque can suddenly rupture, especially where the person suffers from high blood pressure.When a plaque inside a coronary artery ruptures, platelets (blood cells whose function is to stop the bleeding) become sticky, develop tentacles and start to roam around in gangs (platelet aggregation) and quickly make their way to the damaged area and pile on it until they either partially or completely block the artery.
Jiaogulan reduces the affected area and the severity of injury to the brain and heart suffered as a consequence of a stroke or a heart attack, and accelerates the healing and recovery process.95, 96, 97, 98
The herb prevents heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy) and protects heart muscles and their function from damage as a result of diabetes.99, 100
Jiaogulan also helps protect against coronary spasms, irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), pressor response (the increase in arterial blood pressure in response to various internal or external conditions, e.g. drugs, mental stress, etc.), and ventricular tachycardia (a life-threatening rapid heart beat that starts in the bottom pumping chambers of the heart).101
Jiaogulan is beneficial for people who suffer from congestive heart failure because it improves the efficiency of the pumping action of the heart. This means the heart does not work as hard to produce the same amount of blood flow, helping it deliver more oxygen and nutrients to the body as a whole without causing additional stress. 102, 103
Jiaogulan and Cancer
Research has shown that Jiaogulan has many cancer fighting and prevention effects on a wide variety of cancers.
It works on several levels to prevent and heal cancer:
•It enhances the body’s own defences by protecting and boosting the immune system. A strong immune system is important for preventing the formation of tumours.
•With its exceptional antioxidant effects, Jiaogulan scavenges free radicals within the body, minimizing DNA mutations that lead to tumours. (See the Antioxidant section for more information)
•Its chemical components like saponins (gypenosides), flavonoids and polysaccharides have direct anticancer action.
Jiaogulan has been shown in studies to reduce tumour size, inhibit tumour growth and metastasis (spreading), cause apoptosis (tumour cell death) by increasing free-radical damage to cancer cells, and inhibit energy production in cancer cells.
These effects have been demonstrated in several types of cancer, including:
- Liver (hepatoma)104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113
- Lung114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120
- Prostate121
- Colorectal122, 123, 124, 125
- Esophageal 122, 126
- Oral127, 128, 129, 130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135
- Brain136
- Stomach 137, 138
- Skin (melanoma)139, 140
- Uterus/cervix141, 142, 143
- Leukaemia 144, 145, 146, 147
- Sarcoma 147, 148
For those who choose to use the traditional methods of cancer treatment – chemotherapy and radiation therapy – Jiaogulan has shown to be an invaluable ally.
This is because it provides a very strong protection against the damaging effects these treatments have on the immune system.149, 150, 151, 152, 153, 154
Jiaogulan was also found to diminish the overall damaging effects of drug toxicity from chemotherapy137, 148, while at the same time boosting its effectiveness125, 148.
Jiaogulan Slows Down Aging and Increases Longevity
Studies with aging animals have shown that Jiaogulan improves their memory and learning ability 156, and rejuvenates their skin47, 48, 157. It was also found that the herb increases the thickness of the skin, boosts synthesis of collagen, and protects elasticity158. For extra skin benefit, you can also apply Jiaogulan tea topically, for example as a face rinse.
In another study, the lifespan of fruit flies was increased by as much as 50% when given Jiaogulan.160 Other animal studies have also demonstrated increase in lifespan.161, 162
Jiaogulan Prevents and Fights Diabetes Mellitus
• Jiaogulan Decreases Insulin Resistance
Gynostemma improves glucose tolerance by improving the cells’ ability to use insulin to absorb more glucose. 68, 163, 164, 165, 166, 167 It seems to achieve this, at least in part, by inhibiting the activity of an enzyme called protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP1B), which plays a key role in insulin resistance. 168, 169, 170
• Jiaogulan Stimulates Insulin Production
Jiaogulan stimulates insulin release from the pancreas, so that more insulin is available to the body to help cells with absorbing glucose. 171, 172, 173
Jiaogulan Increases Blood Insulin Levels
Jiaogulan increases insulin concentrations in the blood by improving the liver’s capacity to metabolize glucose.165, 173, 174, 175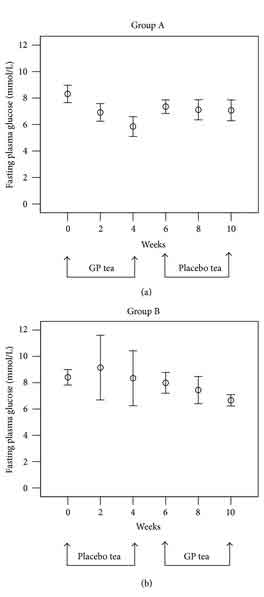
• Jiaogulan Lowers Blood Glucose Levels
Jiaogulan reduces blood glucose levels and inhibits increases in blood glucose after a glucose challenge test. 173, 174, 176
• Jiaogulan Protects From Diabetic Damage
Jiaogulan prevents damage to the cardiovascular system as a result of diabetes.99, 100
In one human clinical study, patients were divided in a placebo and a Jiaogulan treatment group. The two groups did not differ in baseline characteristics and diabetic parameters, and all participants received the same diet and exercise therapies.
Four weeks of treatment were followed by two weeks of no treatment, after which the treatments were reversed so that the placebo-group was given Jiaogulan, and vice versa.
The study found that Gynostemma had the effect of lowering the fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level (the glucose concentration in the blood after at least 8 hours of fasting), while there was no change in the placebo group.Once the treatments were reversed, the former placebo group also showed lower glucose levels.
Meanwhile, the group that was initially treated with Jiaogulan showed lower glucose level during the entire 10-week duration of the trial compared to their levels before the start of the trial.
This happened despite the fact they only took Gynostemma for the first 4 weeks of the 10-week duration of the trial.163
In another clinical study with type 2 diabetes patients, subjects were divided into two groups: one treated with sulfonylurea (an anti-diabetic drug) and Jiaogulan, and another with sulfonylurea and a placebo.
The researchers found that the group using Jiaogulan with sulfonylurea showed lower blood glucose levels and lower insulin resistance compared to the group that was administered sulfonylurea with placebo.
Furthermore, the effect of Jiaogulan and sulfonylurea was comparable to that of using sulfonylurea and metformin, another popular anti-diabetic drug.177
Jiaogulan Protects and Boosts the Immune System
Jiaogulan’s beneficial effects on the immune system are mostly due to its antioxidant properties and ability to balance Nitric Oxide production.
Jiaogulan’s ability to reduce Nitric Oxide when the immune system is overactive is therefore vital in the prevention of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, including some cancers, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, heart disease, periodontitis, and hay fever.
The herb also fights inflammation by decreasing free radical damage and inhibiting Nuclear Factor-kappaB (NF-kB) – a protein involved in cell survival and signaling – both important factors in the generation of inflammation.30, 32, 62, 93, 94, 178, 179, 180, 181
As an antioxidant, the herb protects the integrity of the immune system from free radicals and environmental toxins 26, 30, 32
Gynostemma also protects the immune system from the effects of stress 6, rigorous or exhaustive physical exercise 182, 183, 184, and cancer chemotherapy and radiation therapy149, 150, 151, 152, 153, 154.
Finally, Jiaogulan increases the potency of the immune response to foreign invaders, toxins,6, 30, 185, 186, 187, 188, 189, 190, 191, 192, 193, 194, 195, 196 and cancer 118, 119, 138, 139, 186.
Jiaogulan Protects and Strengthens the Nervous System
Nitric Oxide plays an important role in learning and memory by helping nerve cells in the brain to communicate with each other.197, 198 It is involved in neurotransmitter release, neural development and regeneration, synaptic plasticity and regulation of gene expression.199
At normal concentrations, Nitric Oxide protects the nerve cells from damage and cell death. However, at high concentrations it becomes toxic to the nerve cells and can cause cell injury and cell death.200
Overproduction of Nitric Oxide in the nervous system has been linked to Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Huntington’s disease, and depression.201
In addition, free radical damage has been shown to play a major role in the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.202, 203
In light of this, it’s not surprising that Jiaogulan has been shown to help prevent both Alzheimer’s 204, 205, 206, 207 and Parkinson’s 37, 208, 209, 210, 211, 212, which are the 6th and 14th leading causes of death in the United States respectively. It may also be effective against optic neuritis, although further studies are needed.213
In both human and animal studies, Gynostemma was shown to improve brain functions like memory, concentration, and learning, especially with the elderly.156, 214, 215, 216
The herb also helps protect against and recover from brain and memory damage induced by alcohol217, 218 and free radicals31, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 49, as well as damage and cognitive impairment from ischemia-reperfusion and hypoxia due to stroke and other causes.34, 218, 219, 220, 221, 222, 223, 224, 225, 226, 227
A study with elderly cerebral infarction patients (a type of ischemic stroke) showed that administering Jiaogulan for a 12-week period improved their cognitive functions to a level close to that of normal elderly subjects who had not suffered a stroke. In addition, the improvements were better than that of a control group that was given Piracetam, a popular nootropic and brain-enhancing drug.228
A second clinical study using different evaluation methods showed identical results, and further improvement when treatment was continued for 12 more weeks (24 weeks in total).229
Jiaogulan can also prevent brain and nervous system damage caused by consumption of the popular flavor enhancing food additive Monosodium Glutamate (MSG).230, 231, 232, 233
Lastly, the herb was found to increase the excitability and stability of the brain during athletic competition. A Guiyang Medical College research group carried out testing on more than 300 professional athletes, including athletes of the China National Skating Team.
All of the tested athletes reported that a Jiaogulan/Danshen recipe taken before the competition made them vigorous and alert, with quick reflexes and less nervousness. A control group taking Danshen alone did not feel increased stability and excitability of the nervous system during competition, although they also felt increased energy and endurance.234, 235
Jiaogulan Improves Athletic Performance
Jiaogulan is able to increase athletic performance in several ways:
1. By regulating the production of Nitric Oxide.
2. By improving heart function efficiency.
3. By stimulating the production of the endogenous antioxidants glutathione and superoxide dismutase.
Since one of the main functions of Nitric Oxide is to widen the arteries (vasodilation), it has the effect of increasing blood circulation throughout the body. This provides more of the oxygen and glucose the muscles need to be able to work at peak levels longer, improving stamina and energy levels.
Nitric Oxide also stimulates growth hormone production236, which encourages fat reduction and muscle building.
Jiaogulan also improves the efficiency of the pumping action of the heart, so that it doesn’t work as hard to produce the same amount of blood flow. Again, more oxygen and nutrients reach the muscles and performance is improved.
A clinical study at the Guiyang Medical College with 30 normal healthy persons and 220 athletes showed that within 30 minutes after oral administration of a single dose of Jiaogulan combined with other Chinese medicinal herbs, all subjects responded with increased cardiac output and stroke volume, while heart rate and blood pressure did not change.237
Animal studies have confirmed this positive effect on heart function and have concluded that Jiaogulan’s effect is more potent than that of ginseng 103, 238
A number of studies involving forced swimming tests with animals have proven that Jiaogulan has a significant anti-fatigue effect and increases the endurance capacity in animals, enabling them to swim significantly longer before they get exhausted. In addition, these effects become stronger as the dose is increased.239, 240, 241, 242, 243, 244, 245, 246
Jiaogulan significantly increases glucose levels in the blood, liver and muscles, which is the fuel the muscles use and is therefore very important for the prolongation of endurance exercise.
Furthermore, Gynostemma decreases the amount of lactic acid (the build-up of which causes sore muscles the day after rigorous exercise) in the blood significantly and this is an important indicator for judging the degree of fatigue and means that Jiaogulan is able to postpone the appearance of fatigue and accelerate the recovery from fatigue.239, 240, 241, 242, 243, 244
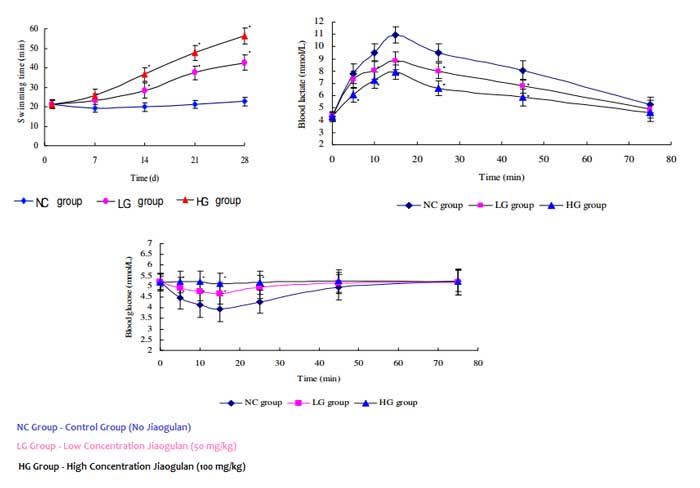
In parallel, the levels of uric nitrogen in the blood are decreased 241, 242, 243, 244, 245, 246, which means that not as much protein needs to be digested in order to produce energy.
Jiaogulan also helps us reach peak mental and physical function by boosting the levels of the endogenous antioxidants superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione, and lowering Malondialdehyde (MDA).241, 243, 244, 245, 246, 247, 248, 249, 250
This means less muscle damage resulting from exercise, quicker recovery time, increased strength, endurance and a shift in the metabolism from fat production to muscle development.Finally, Gynostemma is able to regulate immune function during exercise, recovering immune indices to normal values from either originally lower or higher than the normal.182, 183, 184
This is important because it has been demonstrated that the immune system is suppressed after rigorous exercise. Marathon runners and the high frequency of respiratory tract infections immediately after a run are one example.
If you are involved in physical exercise, act like the pros and have some Jiaogulan before a workout for extra energy and stamina, and after workout to help your body repair more quickly from the damage physical exercise inevitably causes.
Other Health Benefits of Jiaogulan
- Anti-Anxiety and Anti-Stress
Being an adaptogen, Jiaogulan reduces mental and physical stress. It has also been shown to have a significant anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effect and to help recover dopamine and serotonin levels back to normal.6, 211, 251, 252, 253, 254
One double-blind placebo-controlled human clinical trial demonstrated the herb’s ability to significantly reduce anxiety and stress in groups of high anxiety and normal individuals by over 20% and 10% respectively, as evaluated by standard anxiety and stress tests.255
Jiaogulan has also shown promise in the treatment of depression.256 - Promotes Weight Loss
Jiaogulan helps reduce weight in overweight people, at least in part by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK).257, 258 In addition, the herb’s ability to increase insulin sensitivity in the body also has beneficial weight-stabilizing or weight-loss effects.259
A 12-week, randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was done with 80 participants who were considered obese according to Asia-Pacific guidelines. 40 subjects were given an extract of one of Jiaogulan’s active ingredients and 40 were given placebo.
The subjects made no changes to their lifestyle. Body weight in the Jiaogulan group dropped by 1.35kg, fat mass dropped by 1.25kg, and waist circumference dropped by 2.62 centimeters on average. None of these changes were observed in the placebo group.260
A second randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial involving 56 subjects who were diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver also found statistically significant effect of Jiaogulan extract on Body Mass Index (BMI), as well as improvements in other parameters over the placebo group.261
Jiaogulan has also been reported to help those who are underweight to gain mass by improving metabolism and nutrient absorption. However, no studies have yet been done to test this claim.
- Cleanses the Body From Toxins
Jiaogulan has been widely reported to protect and cleanse the body from toxins.294, 295, 296 The herb is able to do that by stimulating the production of the antioxidant glutathione, which plays a vital role in detoxifying the body by binding to pesticides, heavy metals and other toxins until they are excreted.
- Protects the Liver
Jiaogulan was found to completely cure Hepatitis B in a 5.5 years long clinical trial with an effective rate of 77.5%.262 In short-term clinical studies (3 months or less), Jiaogulan was also found to have positive effect on patients with a chronic hepatitis B infection.263, 264
Prevents liver fibrosis – a scarring process that represents the liver’s response to injury – which can lead to cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure and liver cancer.45, 265, 266, 267, 268, 269, 270Effective both as a stand-alone treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease caused by high fat and cholesterol diet271, and as an add-on treatment in a 6 month long human clinical study261. Jiaogulan prevents liver fatty degeneration in fatty liver disease by modulating fat metabolism, ameliorating liver dysfunction, reducing oxidative stress272, and protecting liver cells from injury and death61.
Protects against liver damage and cell death caused by ischemia/reperfusion via its antioxidant activity.273
- Protects and Improves Kidney Function
Three separate clinical studies with hundreds of patients suffering from chronic renal failure showed that Jiaogulan can decrease blood fats and improve kidney function, anaemia, and the nutritional situation in these patients.274, 275, 276
Protects the kidneys from damage due to toxins.277
Suppresses the development of renal fibrosis.278, 279Protects against kidney failure and gout by lowering blood uric acid in cases of hyperuricemia (abnormally high level of uric acid in the blood), which can cause both of these conditions.280
- Fights Respiratory Issues and Supports the Lungs
Jiaogulan is effective against respiratory issues, such as cough, asthma, chronic bronchitis, and chronic tracheitis (inflammation of the trachea).191, 196, 281, 282, 283, 284
In a clinical study of 86 patients with chronic bronchitis, Jiaogulan was found to effectively treat 93% of the cases.285
In another clinical study of 96 cases, Jiaogulan was effective 92% in treating chronic bronchitis.286
The herb is used traditionally as an expectorant and decongestant since it helps clear mucus from the airways, lungs, bronchia and trachea.196
- Protects the Gastro-Intestinal System
Jiaogulan protects the GIT from damage due to toxins277 and improves digestion and metabolism.
It protects against and heals gastric ulcers46, 287, as well as chronic atrophic gastritis288.
It improves bowel movement function and alleviates constipation.Helps regulate the gut microbiome ecosystem by increasing the number of symbiotic bacteria. This may in part contribute to the anticancer effect of Gynostemma, since the gut ecosystem can play an important role in diseases such as cancer, autism, rheumatoid arthritis, and allergies.289
- Balances Hormonal Function
Jiaogulan normalizes and regulates the endocrine/hormonal system, especially adrenal function.2, 300
- Protects and Benefits the Reproductive System
Jiaogulan improves sexual function and helps with Erectile Dysfunction because it regulates Nitric Oxide production. Nitric Oxide plays a key role in developing and maintaining penile erection due to its ability to dilate the arteries and increase blood flow to the whole body, including the penis.209, 290, 291
Increasing Nitric Oxide production is the biological basis of how the popular drug Viagra works.
Nitric Oxide is also important in sperm production and motility, ovarian function and ovulation, oviduct (the tube that links the ovary to the uterus) function, formation of the placenta, pregnancy, labour, sexual behaviour, and generation of steroid hormones.292
Jiaogulan has been shown to protect the sperm from damage due to toxins39 and high blood fat content293. - Treats Insomnia
Gynostemma has been used as an effective treatment for insomnia in folk medicine, especially when it occurs because of excessive stress or anxiety. This is because it soothes the nerves and has anti-stress and anxiety effects on the body. A Guiyang Medical College study with 112 patients showed that Jiaogulan could improve sleep with an effective rate of 89 – 95%.297
- Protects the Skin From Sun Damage
Jiaogulan has been shown to protect from UV radiation when applied directly to the skin.157, 298, 299 Even if consumed only as a tea, the herb will still have a protective effect against sunburn because it’s a powerful antioxidant. This is important in the prevention of melanoma (skin cancer) and premature aging of the skin.
- Helps Against Psoriasis
Jiaogulan has shown promise in the treatment of Psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory skin disorder.301
- Headaches and Migraines
Jiaogulan has been shown to alleviate headaches and migraines.306
-
Hangover
If you ever find you’ve had a few too many drinks the night before, have a couple of cups of Jiaogulan tea in the morning – you’ll be pleasantly surprised!
References
- Guangxi Ribao (Guangxi Daily Newspaper). Chinese. March 4, 1972.
- Winston, David; Steven Maimes (April 2007). Adaptogens: Herbs for Strength, Stamina, and Stress Relief. Healing Arts Press. ISBN 978-1-59477-158-3.
- Dr. Jialiu Liu, Michael Blumert (April 1999). Jiaogulan: China’s “Immortality Herb”–Unlocking the Secrets of Nature’s Powerful Adaptogen and Antioxidant. Torchlight Publishing. ISBN: 978-1-88708-916-6
- Bensky, Dan; Andrew Gamble; Steven Clavey; Erich Stöger (September 2004). Chinese Herbal Medicine: Materia Medica, 3rd Edition. Eastland Press. ISBN 978-0-939616-42-8.
- Liu et al., “Recent Advances on Ginseng Research in China“, Journal of Ethnopharmacology, vol. 36 (1992), pp. 27-38.
- Im, S.-A.; Choi, H.S.; Choi, S.O.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, S.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, C.K.; Restoration of Electric Footshock-Induced Immunosuppression in Mice by Gynostemma pentaphyllum Components. Molecules 2012, 17, 7695-7708.
- Chul Lee, Jin Woo Lee, Qinghao Jin, Hari Jang, Hyun-Jae Jang, Mun-Chual Rho, Myung Koo Lee, Chong Kil Lee, Mi Kyeong Lee, and Bang Yeon Hwang. Isolation and Characterization of Dammarane-Type Saponins from Gynostemma pentaphyllum and Their Inhibitory Effects on IL-6-Induced STAT3 Activation. Journal of Natural Products 2015 78 (5), 971-976 DOI: 10.1021/np500803e
- The Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta Carotine Cancer Prevention Study Group (1994). “The effect of vitamin E and beta carotine on the incidence of lung cancer and other cancers in male smokers“.New England Journal of Medicine 330 (15): 1029–35. DOI:10.1056/NEJM199404143301501. PMID 8127329.
- Omenn GS, Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, Balmes J, Cullen MR, Glass A et al. (1996). “Effects of a combination of beta carotine and vitamin A on lung cancer and cardiovascular disease“.New England Journal of Medicine 334 (18): 1150–5. doi:10.1056/NEJM199605023341802. PMID 8602180.
- Maier CM, Chan PH. Role of superoxide dismutases in oxidative damage and neurodegenerative disorders. Neuroscientist. 2002 Aug;8(4):323-34.
- Fattman CL, Schaefer LM, Oury TD. Extracellular superoxide dismutase in biology and medicine. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003 Aug 1;35(3):236-56.
- Chung JM. The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in persistent pain. Mol Interv. 2004 Oct;4(5):248-50.
- Shin SG, Kim JY, Chung HY, Jeong JC. Zingerone as an antioxidant against peroxynitrite. J Agric Food Chem. 2005 Sep 21;53(19):7617-22.
- Zawadzka-Bartczak E. Activities of red blood cell anti-oxidative enzymes (SOD, GPx) and total anti-oxidative capacity of serum (TAS) in men with coronary atherosclerosis and in healthy pilots. Med Sci Monit. 2005 Sep;11(9):CR440-4.
- Tolmasoff JM, Ono T, Cutler RG. Superoxide dismutase: correlation with life-span and specific metabolic rate in primate species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2777–2781.
- Cutler, R.G. (1985) Peroxide-producing potential of tissues: Inverse correlation with longevity of mammalian species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 4798–4802.
- Li Y, Huang TT, Carlson EJ, Melov S, Ursell PC, Olson JL, Noble LJ, Yoshimura MP, Berger C, Chan PH, Wallace DC, Epstein CJ (December 1995). “Dilated cardiomyopathy and neonatal lethality in mutant mice lacking manganese superoxide dismutase”. Nat. Genet. 11 (4): 376–81. doi:10.1038/ng1295-376. PMID 7493016.
- Andersen HR, Jeune B, Nybo H, et al. Low activity of superoxide dismutase and high activity of glutathione reductase in erythrocytes from centenarians. Age Ageing. 1998 Sep;27(5):643-8.
- Micke P, Beeh KM, Buhl R. Effects of long-term supplementation with whey proteins on plasma glutathione levels of HIV-infected patients. Eur J Nutr. 2002 Feb;41(1):12-8.
- Lang CA, Mills BJ, Lang HL, Liu MC, Usui WM, Richie J Jr, Mastropaolo W, Murrell, SA. High blood glutathione levels accompany excellent physical and mental health in women ages 60 to 103 years. J Lab Clin Med. 2002 Dec; 140(6):380-1.
- IU Li-Bo, HU Bi, LIAO Duan-Fang; Protective effect of gypenosides on free radical damage of isolated guinea pig papillary muscles; Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin; 1993-04.
- Liu, Jialiu. “Effects of a gypenosides-containing tonic on the serum SOD activity and MDA content in middle-aged and aged persons.” Journal of Guiyang Medical College 19.1 (1994): 17.
- Lu, GH. et al. The effect of antioxidant herbs on the erythrocytic SOD activity and serum MDA content in patients with endemic fluorosis. Guizhou Medical Journal 1998; 22(3): 25.
- Zhang, XL et al. Study of the antioxidant effect of Danshen extract in aged persons and patients with fluorosis. Chinese Journal of Endemic Diseases. Chinese. 1998; 17(4):234.
- Ye Hong, Ma Yongxing, Xie Shuzhen, Gan Jiemin; Approaching the antisenescence effect of panglycoside extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum(Thunb) Mak[J];Shanghai Medical & Pharmaceutical Journal;2001-11
- Li, L. and Lau, B. H. S. (1993), Protection of vascular endothelial cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidant injury by gypenosides, saponins of Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Phytotherapy Research, 7: 299–304. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2650070408
- Yuan Quan, Yijun Yang, Huixing Wang, Bo Shu, Qi-hai Gong, Minzhang Qian. Gypenosides attenuate cholesterol induced DNA damage by inhibiting the production of reactive oxygen species in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Molecular Medicine Reports. 12/2014; 11(4). DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2014.3095
- Zhou L, Xu YP, Wei Y, Shi XP, Liu CP. The effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (GP) on plasma lipoprotein metabolism and lipoperoxidation lipoprotein in the experimental hyperglycemia rats. Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology [2008, 24(2):205-208]
- L Li, L Jiao, B H Lau. Protective effect of gypenosides against oxidative stress in phagocytes, vascular endothelial cells and liver microsomes. Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Loma Linda University, CA. Cancer biotherapy 02/1993; 8(3):263-72. DOI: 10.1089/cbr.1993.8.263
- Lou Zhenling; Ma Liping; Zhang Xiaoqin, et al; Study on Biological Effects of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Makino Polysaccharide (GPS)[J];Henan Journal of Oncology;1996-03
- WANG Qiugui; CHENG Yewen et al; Effects of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum on the Contents of SOD, GSH-PX, MDA, LDH and ATPase in Brain, Heart and Kidney of Severely Burned Rats[J];Journal Of Xianning Medical College;1999-04
- YAO Dan-dan,HUANG Shan-hua; Study on the anti-aging function of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino on sub-aging rats[J];Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine;2007-28
- Cheng, YH et al. The effect of antioxidant Chinese herbs on SOD activity, MDA content and ultrastructural damage of the kidney tissue in mice with chronic fluorosis. Chinese. Guizhou Yiyao (Guizhou Medical Journal) 1998; 22(2): 94.
- Zhang, Guang-Lin et al. Gypenosides improve cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats by suppressing oxidative stress and astrocytic activation. Behavioural Pharmacology: October 2011 – Volume 22 – Issue 7 – p 633–644 doi: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e32834afef9
- L. Schild,T. Cotte,G. Keilhoff,R. Brodemann. Preconditioning of brain slices against hypoxia induced injury by a Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract – Stimulation of anti-oxidative enzyme expression. Phytomedicine: 15 June 2012, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2012.03.012
- Jiang Enping et al. Protective effects of gypenosides on PC12 cell injury induced by oxidative stress. Human Health and Biomedical Engineering (HHBE), 2011 International Conference on, IEEE, 19-22 Aug. 2011, p.410-413 10.1109/HHBE.2011.6027986
- Wang P, Niu L, Gao L, Li WX, Jia D, Wang XL, Gao GD. Neuroprotective effect of gypenosides against oxidative injury in the substantia nigra of a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Journal of International Medical Research, 2010 May-Jun;38(3):1084-92.
- LIU Guohui,YAO Dandan,LU Jiayi,et al; The Effect Mechanism of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Makino to Hippocampus in Aged Rats Induced by D-galactose;The Journal of Medical Theory and Practice;2006-05
- Yuan H et al. Gynostemma pentaphyllum protects mouse male germ cells against apoptosis caused by zearalenone via Bax and Bcl-2 regulation. Toxicology Mechanisms and Methods, 2010 Mar;20(3):153-8. doi: 10.3109/15376511003660185
- YAN Yan,GUO Jie,YANG Fei,XUE Wei; Anti-Oxidative Effect of Gynostemma and Hawthorn Extracts on the Aging Mouse Model Induced by D-galactose;Laboratory Animal Science;2009-03
- Chun-Ching Lin, Pei-Chen Huang, and Jer-Min Lin, Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Anoectochilus formosanus and Gynostemma pentaphyllum. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 28, 87 (2000). DOI: 10.1142/S0192415X00000118
- Ye Zhenjun et al; Inhibitory Effect Of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum(Gp) On Liver Lipid Peroxidation Caused By Ccl_4;Industrial Health And Occupational Diseases;1998-02
- XIAO Zeng-ping, JI Ai-guo, SONG Shu-liang, LIANG Hao, LIU Ying-ying; Protective effects of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum polysaccharide on CCl_4-induced liver injury in mice; Chinese Journal of Biochemical Pharmaceutics;2008-03
- H. Huang, B. Qi, Protective Role of Polysaccharides from Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino Supplementation against Exhaustive Swimming Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress in Liver and Skeletal Muscle of Mice, Advanced Materials Research, Vols. 962-965, pp. 1231-1234, Jun. 2014
- Feng Q, Li X, Peng J, Duan X, Fu Q, Hu Y. Effect of gypenosides on DMN-induced liver fibrosis in rats. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2012 Feb;37(4):505-8.
- ZHANG Qing Bei, MA Jun Jiang, CHAO Zhi Xian, LIN Zhi Bin; Therapeutic role and its mechanism of gypenosides on delayed healing of experimental gastric ulcer induced by NCTC11637 strain HP in rats;Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin;1999-03
- YIN Ying,WU Jing-dong,GU Wei. The Chinese native medicine G.Pentaphyllum extraction resistance mouse skin senile experimental study. Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Medicine; 2008-06
- WANG Cai-xia,WANG Li-xin; The Experiment Study on Gynostemma External Skin Tissue on the Natural Aging Mice,CAT Activity,MDA Content; Journal of Practical Traditional Chinese Internal Medicine; 2011-07
- YAO Dandan, HUANG Shanhua, LIU Guohui; Effects of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Makino on Hypothalamus in Aging Rats and Its Mechanisms; The Journal of Medical Theory and Practice; 2007-1
- Wang HongFang, Li ChangJun, Wu XiaoLan; Lou XiaoJuan; Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino polysaccharides supplementation on exercise tolerance and oxidative stress induced by exhaustive exercise in rats.; African Journal of Agricultural Research 2012 Vol. 7 No. 17 pp. 2632-2638
- Li ChangJun et al; Protective effects of crude polysaccharide from Gynostemma pentaphyllum on swimming exercise-induced oxidative stress in rat.; Journal of Animal and Veterinary Advances 2012 Vol. 11 No. 10 pp. 1627-1632
- Gao D, Zhao M, Qi X, Liu Y, Li N, Liu Z, Bian Y; Hypoglycemic effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins by enhancing the Nrf2 signaling pathway in STZ-inducing diabetic rats.; Archives of Pharmacal Research; 2014 Jul 29.
- Zhuohong Xie et al.; Chemical Composition of Five Commercial Gynostemma pentaphyllum Samples and Their Radical Scavenging, Antiproliferative, and Anti-inflammatory Properties.; Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry; 2010 Nov 10;58(21):11243-9. doi: 10.1021/jf1026372. Epub 2010 Oct 12.
- L. Schild et al.; Selective induction of apoptosis in glioma tumour cells by a Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract; Phytomedicine; Volume 17, Issues 8–9, July 2010, P. 589–597
- LIU Qing-qing, WU Jing-dong; Effect of Extract of Gynostemma on Activities of SOD and Capacity of Inhibiting OH in Blood of Naturally Senile Mice;Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine;2008-06
- Cai Taisheng, Zhang Shan-feng, Wang Ming-chen; Anti-oxidation effect of gypenosides in aged rats; Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation; 2005-35
- HUANG Hong-Lin et al; Effect of Gypenosides on Formation of Atherosclerotic Plaque of Aorta in Hypercholesterolemic Rabbits; Chinese Journal Of Arteriosclerosis; 1998-04
- DE Koshland Jr, “The molecule of the year”, Science 18 December 1992: Vol. 258 no. 5090 p. 1861 DOI: 10.1126/science.1470903
- HUANG Hong Lin, CHEN Lin Xi, ZHU Bin Yang, YU Lin, LIAO Duan Fang; Effects of gypenosides on c sis expression of bovine aortic endothelial cells and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells induced by lipopolysaccharide and active oxygen species; Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin; 1999-04
- Miles A. Tanner, Xin Bu, J.Alan Steimle, Paul R. Myers. The Direct Release of Nitric Oxide by Gypenosides Derived from the Herb Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Nitric Oxide, Volume 3, Issue 5, October 1999, Pages 359-365
- Muller C, Gardemann A, Keilhoff G, Peter D, Wiswedel I, Schild L.; Prevention of free fatty acid-induced lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, and cell death in primary hepatocyte cultures by a Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract.; Phytomedicine; 2012 Mar 15;19(5):395-401. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2011.12.002. Epub 2012 Feb 29.
- Aktan F, Henness S, Roufogalis BD, Ammit AJ; Gypenosides derived from Gynostemma pentaphyllum suppress NO synthesis in murine macrophages by inhibiting iNOS enzymatic activity and attenuating NF-kappaB-mediated iNOS protein expression.; Nitric Oxide. 2003 Jun;8(4):235-42.
- Tang Chaoke, Sun Ming, Wen Gebo, Hu Bi, Liao Duanfang; Effect of Gypenosides on Mean Arterial Pressure and Nitric Oxide Levels in Rabbits with Endotosin Induced Shock; Journal Of Hengyang Medical College;1999-04
- TANG Chao ke, HU Bi,LIAO Duan fang; Effect of Gypenosides on hemodynamics and nitric oxide in rabbits injected with endotoxin; Chinese Heart Journal;2000-05
- Lu, GH. et al. Comparative study on anti-hypertensive effect of Gypenosides, Ginseng and Indapamide in patients with essential hypertension. Guizhou Medical Journal 1996; 20:1.
- Wang M, Wang F, Wang Y, Ma X, Zhao M, Zhao C (2013) Metabonomics Study of the Therapeutic Mechanism of Gynostemma pentaphyllum and Atorvastatin for Hyperlipidemia in Rats. PLoS ONE 8(11): e78731. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078731
- Samer Megalli, Fugen Aktan, Neal M. Davies, Basil D. Roufogalis; Phytopreventative Anti-Hyperlipidemic Effects Of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum In Rats; J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci (www.cspscanada.org) 8(3):507-515, 2005
- Samer Megalli, Neal M. Davies, and Basil D. Roufogalis; Anti-Hyperlipidemic and Hypoglycemic Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in the Zucker Fatty Rat; J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci (www.cspscanada.org) 9(3):281-291, 2006
- Ma Pingbo, Zhu Quanhong, Huang Zhongwei; Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum on the blood-lipid and hemorheology in hyperlipidemia rabbits; The Chinese Pharmaceutical Association [2005, 22(6):454-455]
- Zhou L, Xu YP, Wei Y, Shi XP, Liu CP; The effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (GP) on plasma lipoprotein metabolism and lipoperoxidation lipoprotein in the experimental hyperglycemia rats; Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology [2008, 24(2):205-208]
- Zhang Weiping, Ma Yuting, Xu Hua; Study on antiblood -fat of rats experimental hyperoipoidmia with drill pill of Gynostemma pentaphyllum; Nei Mongol Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 2004-02
- Tan Huabing; Effect of Fiveleaf Gynostemma Herb on hyperlipoidemia and hemorheological changes in rabbits; Medical Department, The People’s Hospital of Yunyang Medical College.Shiyan 442000,Hubei;China
- Tan Huabing, He Qin; The Effect of Fiveleaf Gynostemma Herb on the Level of Testosterone in Male Rabbits; Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio-/Cerebrovascular Disease; 2006-12
- Chen Guilin et al.; Study on Hypolipidemic and Antioxidation Action of 50% Ethanol Fraction in Gynostemma Pentaphyllum; China Pharmaceuticals; 2012-15
- TAN Hua-bing,KUANG Ying-wen; Interfering effect of Gynostemma pentaphillia on atherosclerosis caused by high cholesterol diet in rabbits; Shanxi Medical Journal; 2006-10
- TAN Huabing,LU Side,ZHONG Xiaodong; Research of interference effect of Fiveleaf Gynostemma Herb on hyperlipomia and C-reaction protein rise in the rabbits caused by rich hypercholesterolemia diet; Journal of Practical Diagnosis and Therapy; 2006-11
- Huang TH, Razmovski-Naumovski V, Salam NK, Duke RK, Tran VH, Duke CC, Roufogalis BD; A novel LXR-alpha activator identified from the natural product Gynostemma pentaphyllum.; Biochemical Pharmacology; 2005 Nov 1;70(9):1298-308.
- Razmovski-Naumovski, Valentina; Characterisation of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Saponins Affecting Cholesterol Homeostasis; Diss. Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Sydney, 2005.
- Ky, P. T., et al. “Cholesterol-lowering effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb) Makino.” TAP CHI DUOC HOC-SAIGON THEN HANOI-5 (2007): 9.
- Practical Applications of Modern Herbal Medicine 1990;7(1):42.,
- Hunan Medicine 1991;8(5):259.
- La Cour B, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of hyperlipidemia. Journal of Ethnopharmacology May 1996;46(2):125-9.)
- Hu X, et al. Antilipemic effect Gynostemma pentaphyllum in patients. Fujian Medical Journal . 1988; 10(5):4–6.
- Zhou H, et al. Treatment of hyperlipidemia with Gynostemma pentaphyllum Jiaogulan. Hunan Med J . 1991; 8(5):259–60.
- Huang TH, Tran VH, Roufogalis BD, Li Y; Gypenoside XLIX, a naturally occurring gynosaponin, PPAR-alpha dependently inhibits LPS-induced tissue factor expression and activity in human THP-1 monocytic cells.; Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology; 2007 Jan 1;218(1):30-6. Epub 2006 Oct 25.
- Yu Juan, Yang Shanzhang; Observation of Effects of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum on Platelet Disaggregation in Human; Journal Of Fujian Medical University; 1995-03
- Zhang Xiaoli et al.; Influence Of Gypenosides On Thrombus And Coagulation Function In Vivo And In Vitro; West China Journal Of Pharmaceutcal Sciences; 1999-Z1
- Ci Mingyu,Zhang Zhengbo,Zhen Guiyuan et al.; Study the Effect of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Makin in Restraining Thrombosis in Vivo of Experimental Mice; Journal of Practical Traditional Chinese Medicine; 2003-11
- Tan H, Liu ZL, Liu MJ; Antithrombotic effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum; Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine; [1993, 13(5):278-80, 261]
- QiGang Li, Changlin Ma, Jian SuYaMin; THE INFLUENCE OF GYPENOSIDE(GP) ON PLATELET AGGREGATION AND THROMBOSIS; Acta Academiae Medicinae Cpapf; 1995-01
- WU Ji-Liang,QIU Pei-Lun,LIU Jun-Tian,MU Qi-Yun,XIN Dong-Sheng; Effects of gypenosides on platelet aggregation release and cAMP level in rabbits; Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology; 1990-01
- Li Lin, Jin Youyu; THE INFLUENCE OF JIAOGULAN EXTRACT ON PLATELET AGGREGATION AND ARACHIDONATE METABOLISM IN RABBITS; Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin; 1989-04
- Huang TH, Tran VH, Roufogalis BD, Li Y; Gypenoside XLIX, a naturally occurring PPAR-alpha activator, inhibits cytokine-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression and activity in human endothelial cells.; European Journal of Pharmacology; 2007 Jun 22;565(1-3):158-65. Epub 2007 Mar 24.
- Quan Y, Qian MZ; Effect and mechanism of gypenoside on the inflammatory molecular expression in high-fat induced atherosclerosis rats; Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi; 2010 Apr;30(4):403-6.
- Liao Duan Fang et al.; Effect of Gypenosides against Oxidative Damage. Part 2 the Influence of Gypenosides on Cerbrovascular Injury Induced by Free Radicals; Department of Pharmacology; 1993-03
- Wang XJ et al.; Gypenosides pre-treatment protects the brain against cerebral ischemia and increases neural stem cells/progenitors in the subventricular zone; International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience; 2014 Apr;33:49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 12.
- Xiong WS, Yan XD, Shen N, Qiu FL, Chen X; Protective effects of gypenosides on experimental myocardial infarction; Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1990 Sep;11(5):427-30.
- Le L, Gao XL, Ding BX, Yuan BX; Effect of total flaveos of Gymostemma pentaphyllum on protein expression of Fas/FasL genes and TNF-alpha concentration in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes with hypoxia-reoxygenation; Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2007 Sep;32(18):1925-7.
- Ge M, Ma S, Tao L, Guan S; The effect of gypenosides on cardiac function and expression of cytoskeletal genes of myocardium in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats; American Journal of Chinese Medicine; 2009;37(6):1059-68.
- GE Min ,LIU Tong, GUAN Su-dong, MA Shan-feng, WU Ying-liang; Effects of gypenosides on cardiac function in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats; Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University; 2007-06
- Circosta C, De Pasquale R, Occhiuto F; Cardiovascular effects of the aqueous extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino; Phytomedicine. 2005 Sep;12(9):638-43.
- Zhou, Ying-Na et al. Effects of a gypenosides-containing tonic on the pulmonary function in exercise workload. Journal of Guiyang Medical College 1993 18 (4):261.)
- Li Y, et al. Effects of total gypenosides on heart function and blood pressure of rabbits. Acta Academiae Medicinae Shandong . 1990; 28(3):34–36.
- Tsai YC, Lin CL, Chen BH; Preparative chromatography of flavonoids and saponins in Gynostemma pentaphyllum and their antiproliferation effect on hepatoma cell; Phytomedicine. 2010 Dec 15;18(1):2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2010.09.004. Epub 2010 Oct 30.
- Wang QF, Chen JC, Hsieh SJ, Cheng CC, Hsu SL; Regulation of Bcl-2 family molecules and activation of caspase cascade involved in gypenosides-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma cells; Cancer Letters; 2002 Sep 26;183(2):169-78.
- Wang QF, Chiang CW, Wu CC, Cheng CC, Hsieh SJ, Chen JC, Hsieh YC, Hsu SL; Gypenosides induce apoptosis in human hepatoma Huh-7 cells through a calcium/reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial pathway; Planta Medica; 2007 Jun;73(6):535-44. Epub 2007 May 22.
- Chen JC, Chung JG, Chen LD; Gypenoside induces apoptosis in human Hep3B and HA22T tumour cells; Cytobios; 1999;100(393):37-48.
- Liu J, Zhang L, Ren Y, Gao Y, Kang L, Qiao Q; Anticancer and immunoregulatory activity of Gynostemma pentaphyllum polysaccharides in H22 tumor-bearing mice; International Journal of Biological Macromolecules; 2014 Aug;69:1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.05.014. Epub 2014 May 12.
- Tsai YC, Wu WB, Chen BH; Preparation of carotenoids and chlorophylls from Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino and their antiproliferation effect on hepatoma cell; Journal of Medicinal Food; 2010 Dec;13(6):1431-42. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2010.1165. Epub 2010 Oct 14.
- Piao XL, Xing SF, Lou CX, Chen DJ; Novel dammarane saponins from Gynostemma pentaphyllum and their cytotoxic activities against HepG2 cells; Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters; 2014 Oct 15;24(20):4831-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.08.059. Epub 2014 Sep 4.
- Jun Liu,Lihua Zhang,Yingang Ren,Yanli Gao,Li Kang,Qing Qiao; Anticancer and immunoregulatory activity of Gynostemma pentaphyllum polysaccharides in H22 tumor-bearing mice; International Journal of Biological Macromolecules; Volume 69, August 2014, Pages 1–4
- CAO Jian-guo, ZHOU Jun-min, TANG Xiao-qing, et al.; Gypenosides promotes the programmed cell death of human liver carcinoma cells; Chinese Journal Of Cancer; 1999-S1
- Chen Wei, Li GuangYuan; The Effects Of Gypenosides On Nucleic Acid And Protein In Culture Hepatoma Cell; Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University(Medical Sciences); 1993-01
- Ko-Chung Tsui et al.; Flavonoids from Gynostemma pentaphyllum Exhibit Differential Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest in H460 and A549 Cancer Cells; Molecules 2014, 19(11), 17663-17681; doi:10.3390/molecules191117663
- Lu HF et al.; Gypenosides induced G0/G1 arrest via inhibition of cyclin E and induction of apoptosis via activation of caspases-3 and -9 in human lung cancer A-549 cells; In Vivo. 2008 Mar-Apr;22(2):215-21.
- Chen DJ, Liu HM, Xing SF, Piao XL; Cytotoxic activity of gypenosides and gynogenin against non-small cell lung carcinoma A549 cells; Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters; 2014 Jan 1;24(1):186-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.11.043. Epub 2013 Nov 26.
- Piao XL, Wu Q, Yang J, Park SY, Chen DJ, Liu HM; Dammarane-type saponins from heat-processed Gynostemma pentaphyllum show fortified activity against A549 cells; Archives of Pharmacal Research; 2013 Jul;36(7):874-9. doi: 10.1007/s12272-013-0086-6. Epub 2013 Mar 19.
- LIU Xia, WANG Ping-jun, Xu Fu-xin; Study On Gypenosides Inhibiting Neoplasm Growth And Elevating Immunological Function In Lewis Lung Cancer Of Mice; Journal of Anhui Traditional Chinese Medical College; 2001-01
- Liang Jun,Tang Xiaofang, Wei Xiaolong; Effects of gypenosides on neoplasm growth and immunity function of Lewis lung neoplasm grafted mice; The Journal Of Pharmaceutical Practice; 1999-05
- Liu, J.-S., Chiang, T.-H., Wang, J.-S., Lin, L.-J., Chao, W.-C., Inbaraj, B. S., Lu, J.-F. and Chen, B.-H. (2015), Induction of p53-independent growth inhibition in lung carcinoma cell A549 by gypenosides. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 19: 1697–1709. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12546
- Cheng TC, Lu JF, Wang JS, Lin LJ, Kuo HI, Chen BH; Antiproliferation effect and apoptosis mechanism of prostate cancer cell PC-3 by flavonoids and saponins prepared from Gynostemma pentaphyllum; Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry; 2011 Oct 26;59(20):11319-29. doi: 10.1021/jf2018758. Epub 2011 Sep 26.
- Yan H, Wang X, Wang Y, Wang P, Xiao Y; Antiproliferation and anti-migration induced by gypenosides in human colon cancer SW620 and esophageal cancer Eca-109 cells; Humand and Experimental Toxicology; 2014 May;33(5):522-33. doi: 10.1177/0960327113497771. Epub 2013 Jul 30.
- Yan H, Wang X, Niu J, Wang Y, Wang P, Liu Q; Anti-cancer effect and the underlying mechanisms of gypenosides on human colorectal cancer SW-480 cells; PLoS One; 2014 Apr 21;9(4):e95609. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095609. eCollection 2014.
- Chen JC, Lu KW, Lee JH, Yeh CC, Chung JG; Gypenosides induced apoptosis in human colon cancer cells through the mitochondria-dependent pathways and activation of caspase-3; Anticancer Research; 2006 Nov-Dec;26(6B):4313-26.
- William Chi, Shing Tai, Wing Yan Wong, Jen Fu Chiu, and Wen Luan Wendy Hsiao; Mechanistic investigation of the anti-cancer and anti-hyperlipidemia effects of Gynostemma triterpenoids using systems biology approach; The Journal of Cancer Research; July 1, 2012 72; A24; doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.CSB12-A24
- Wang C, Wang X, Li Y, Deng S, Jiang Y, Yue L; A preliminary observation of preventive and blocking effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb) Makino on esophageal cancer in rats; Journal of West China University of Medical Sciences; [1995, 26(4):430-432
- Zhou Z, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Zhang S; Effect of gynostemma pentaphyllum mak on carcinomatous conversions of golden hamster cheek pouches induced by dimethylbenzanthracene: a histological study; Chinese Medical Journal (Engl). 1998 Sep;111(9):847-50.
- Zhou Z, Wang Y, Zhou Y; The effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum mak (GP) on carcinogenesis of the golden hamster cheek pouch induced by DMBA; Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1996 Sep;31(5):267-70.
- Lu KW et al.;Gypenosides suppress growth of human oral cancer SAS cells in vitro and in a murine xenograft model: the role of apoptosis mediated by caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways; Integrative Cancer Therapies; 2012 Jun;11(2):129-40. doi: 10.1177/1534735411403306. Epub 2011 Jun 10.
- Chen JC et al.; Gypenosides induced G0/G1 arrest via CHk2 and apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondria-dependent pathways in human tongue cancer SCC-4 cells; Oral Oncology; 2009 Mar;45(3):273-83. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2008.05.012. Epub 2008 Jul 31.
- Lu KW et al.; Gypenosides inhibits migration and invasion of human oral cancer SAS cells through the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 -9 and urokinase-plasminogen by ERK1/2 and NF-kappa B signaling pathways; Human and Experimental Toxicology; 2011 May;30(5):406-15. doi: 10.1177/0960327110372405. Epub 2010 May 28.
- Lu KW et al.; Gypenosides causes DNA damage and inhibits expression of DNA repair genes of human oral cancer SAS cells; In Vivo. 2010 May-Jun;24(3):287-91.
- Lu KW et al; Gypenosides inhibited invasion and migration of human tongue cancer SCC4 cells through down-regulation of NFkappaB and matrix metalloproteinase-9.; Anticancer Research, 2008 Mar-Apr;28(2A):1093-9.
- Zhou Zengtong, Tang Guoyao, Zhong Wenjing, et al.; Experimental study on the influence of Gynostemma pentaphyllam Mak upon point mutation of Ha ras oncogene in blocking leukoplakia from canceration; Chinese Journal Of Stomatology; 2000-02
- LOU Jia-ning,GE Shu-yun,ZHOU Zeng-tong; The study of altered succinate dehydrogenase gene expression by Gypenosides during rat tongue OLK carcinogenesis induced by 4-Nitroquinoline 1-Oxide; Journal of Clinical Stomatology; 2010-12
- Schild L, Chen BH, Makarov P, Kattengell K, Heinitz K, Keilhoff G; Selective induction of apoptosis in glioma tumour cells by a Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract; Phytomedicine. 2010 Jul;17(8-9):589-97. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2009.12.002. Epub 2010 Jan 27.
- Yin Xiangmin Yu Xinmin et al.; Study on Therapeutic Effect of Treating Moderate and Advanced State Gastric Cancer by the Compound Jiaogulan; Journal of Heze Medical College; 1999-04,
- Wan Jijin Ge Zhenhua et al.; The Effects of Gynostenmma Pentaphyllum on Proliferation & Immunity of Tumor Cells; Journal of Fujian College of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 1993-03
- Li XL, Wang ZH, Zhao YX, Luo SJ, Zhang DW, Xiao SX, Peng ZH; Isolation and antitumor activities of acidic polysaccharide from Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino; Carbohydrate Polymers; 2012 Jul 1;89(3):942-7. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.04.040. Epub 2012 Apr 21.
- Hye In Lee, Byoung Sam Yoo, Mi Ae Yoo, Sang Yo Byun; Inhibition of melanogenesis and melanin transportation by Gynostemma pentaphyllum; Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering; July 2007, Volume 24, Issue 4, pp 655-659
- Chiu TH, Chen JC, Chen LD, Lee JH, Chung JG; Gypenosides inhibited N-acetylation of 2-aminofluorene, N-acetyltransferase gene expression and DNA adduct formation in human cervix epithelioid carcinoma cells (HeLa); Research Communications in Molecular Pathology and Pharmacology; 2004;115-116:157-74.
- Chiu TH, Chen JC, Chung JG; N-acetyltransferase is involved in gypenosides-induced N-acetylation of 2-aminofluorene and DNA adduct formation in human cervix epidermoid carcinoma cells (Ca Ski); In Vivo. 2003 May-Jun;17(3):281-8.
- Miao GAO, Juan-juan LIU, Dong WANG; The anti-proliferation effect of gypenosides on cervical cancer HeLa cells and its molecular mechanism; Tumor; Vol 33, No 10 (2013); DOI:10.3781/j.issn.1000-7431.2013.10.004
- Lin JJ et al.; Molecular evidence of anti-leukemia activity of gypenosides on human myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells in vitro and in vivo using a HL-60 cells murine xenograft model; Phytomedicine. 2011 Sep 15;18(12):1075-85. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2011.03.009. Epub 2011 May 18.
- Yang L, Wang P, Cheng XX, Zhang MY, Xiao YP; Suppressive effect of gypenosides on murine leukemia L1210 cell lines; Zhong Yao Cai. 2010 Oct;33(10):1588-92.
- Hsu HY et al.; An experimental study on the antileukemia effects of gypenosides in vitro and in vivo; Integrative Cancer Therapies; 2011 Mar;10(1):101-12. doi: 10.1177/1534735410377198. Epub 2010 Aug 11.
- Xu Changfu, Wang Bing, Ren Shuting, et al.; The suppressive effect of gypenosides on murine S_(180) sarcoma and cultured erythroleukemia cell line K_(562); Journal of Xi’an Medical University(Chinese); 2002-03
- Xu Changfu, Yang yanping, Wang Bing et al.; The Suppression Effect Of Gypenosides,Adriamycin And 5-Fluorouracil Combination Therapy On S_(180) Sarcoma; Journal Of Xi’an Medical University(Chinese); 1996-02
- Qian Hao, Fu Shen, Jiang Guoliang, Wang Lijuan, Fu Xiaolong, Ye Ming, Zhao Sen; Protective Effect Of Jiaogulan On Cellular Immunity Of The Patients With Primary Lung Cancer Treated By Radiotherapy Plus Chemotherapy; Acta Atademiae Medicinae Shanghai; 1995-05
- Liu Shao-xiang, Hou Jun, Chen zhi-feng et al.; Experimental and Clinical Study on Treatment of Cancer with Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Makino; Chinese Journal Of Surgery Of Integrated Traditional And Western Medicine; 1996-02
- Wang, HR et al. Therapeutic and tonic effects of jiaogulan on leukopenic patients. Xin Zhong Yi (Chinese); 1991; 23(1): 36.
- Liu, et al. Therapeutic effect of jiaogulan on leukopenia due to irradiation and chemotherapy. Zhong Guo yi Yao Xue Bao (Chinese); 1992; 7(2): 99. )
- Hou, J., et al. “Effects of gynostemma pentaphyllum makino on the immunological function of cancer patients.” Journal of traditional Chinese Medicine, Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine 11.1 (1991): 47-52.
- Wang J, et al. Immunological effects of jiaogulan granule in 19 cancer patients; Zhejiang Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 1989; 24(10): 449
- Hunan Journal of Medicine and Herbology 1991; 7(2): 56.)
- Gao Nannan, Yu Shuren, Lu Ruijian; Improving the learning and, memory ability on aging rats by gypenosides; Chinese Journal Of Gerontology; 1995-06
- Sara Nadia Lobo, Yu Qing Qi, and Quan Zhong Liu, “The Effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Extract on Mouse Dermal Fibroblasts” ISRN Dermatology, vol. 2014, Article ID 202876, 6 pages, 2014. doi:10.1155/2014/202876
- CONG Jing; Morphological Changes of Aging Skin of Mice Effected by Fiveleaf Gynostemma Herb; Journal of Shenyang Medical College; 2007-02
- Study of Chinese Patent Medicine 1988; 10(3): 25.
- Chen Jue, Xu Hengjun; Effect Of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum On The Life Span Of Fruit Fly; Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin; 1987-06
- Chen Qingyao, Ji Yuantang, Sun Yulin; Biological effect of fiveleaf gynostemma (Gynostemma pentaphyllum); Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs [1995, 26(10):527-528]
- Li Fuen et al.; Study Of Effect Of Gynostemma Complex On Prolonging Life; Journal Of Binzhou Medical College; 1997-05
- Huyen VT, Phan DV, Thang P, Hoa NK, Ostenson CG; Gynostemma pentaphyllum Tea Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Type 2 Diabetic Patients; Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism; 2013;2013:765383. doi: 10.1155/2013/765383. Epub 2013 Jan 31.
- Huyen VT, Phan DV, Thang P, Hoa NK, Ostenson CG; Antidiabetic effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum tea in randomly assigned type 2 diabetic patients; Hormone and Metabolic Research; 2010 May;42(5):353-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1248298. Epub 2010 Mar 8.
- Zhang HJ, Ji BP, Chen G, Zhou F, Luo YC, Yu HQ, Gao FY, Zhang ZP, Li HY; A combination of grape seed-derived procyanidins and gypenosides alleviates insulin resistance in mice and HepG2 cells; Journal of Food Science; 2009 Jan-Feb;74(1):H1-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00976.x.
- Yassin K, Huyen VTT, Hoa KN, Östenson CG. Herbal Extract of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Decreases Hepatic Glucose Output in Type 2 Diabetic Goto-Kakizaki Rats; International Journal of Biomedical Science : IJBS. 2011;7(2):131-136.
- Waranya Keapai, Sopida Apichai, Narissara Lailerd, Anchalee Pongchaidecha; Attenuation of Hyperglycemia and Hyperlipidemia in High Fat Diet and Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats by Aqueous Extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum; 12th Graduate Research Conference, Khon Kaen University, Thailand; 2011.
- Zhang XS, Bi XL, Wan-Xiao, Cao JQ, Xia XC, Diao YP, Zhao YQ; Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory effect by dammarane-type triterpenes from hydrolyzate of total Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins; Bioorganic and Medical Chemistry Letters; 2013 Jan 1;23(1):297-300. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.10.097. Epub 2012 Nov 1.
- Xu JQ, Shen Q, Li J, Hu LH; Dammaranes from Gynostemma pentaphyllum and synthesis of their derivatives as inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry; 2010 Jun 1;18(11):3934-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.04.073. Epub 2010 Apr 28.
- Hung TM, Hoang DM, Kim JC, Jang HS, Ahn JS, Min BS; Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory by dammaranes from Vietnamese Giao-Co-Lam tea; Journal of Ethnopharmacology; 2009 Jul 15;124(2):240-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.04.027. Epub 2009 May 3.
- Ake Norberg et al.; A Novel Insulin-releasing Substance, Phanoside, from the Plant Gynostemma pentaphyllum; The Journal of Biological Chemistry; October 1, 2004; 279, 41361-41367; doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403435200
- Hoa NK, Norberg A, Sillard R, Van Phan D, Thuan ND, Dzung DT, Jörnvall H, Ostenson CG; The possible mechanisms by which phanoside stimulates insulin secretion from rat islets; The Journal of Endocrinology; 2007 Feb;192(2):389-94.
- Lokman; Anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects of medicinal plants in a type 2 diabetic animal model; Doctoral Thesis, Kirurgisalen, Karolinska University Hospital, Solna; 2015
- Yeo J, Kang YJ, Jeon SM, Jung UJ, Lee MK, Song H, Choi MS; Potential hypoglycemic effect of an ethanol extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice; Journal of Medicinal Food; 2008 Dec;11(4):709-16. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2007.0148.
- DU Xiao-yan, HOU Ying, TAN Hua, HAN Yan, ZHANG Yan; Hypoglycemic Activity of Polysaccharide from Gynostemma pentaphyllum on Type 2 Diabetic Rats and its Mechanism; Science Technology and Engineering; 2011-24
- Hoa, N.K., Phan, D.V., Thuan, N.D., Ostenson, C.-G; Screening of the hypoglycemic effect of eight Vietnamese herbal drugs; Methods and Findings in Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology; 2009, 31(3): 165; DOI: 10.1358/mf.2009.31.3.1362514
- Huyen VT, Phan DV, Thang P, Ky PT, Hoa NK, Ostenson CG; Antidiabetic Effects of Add-On Gynostemma pentaphyllum Extract Therapy with Sulfonylureas in Type 2 Diabetic Patients; Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine; 2012; 2012:452313. doi: 10.1155/2012/452313. Epub 2012 Oct 17.
- Yang F, Shi H, Zhang X, Yu LL; Two novel anti-inflammatory 21-nordammarane saponins from tetraploid Jiaogulan (Gynostemma pentaphyllum); Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry; 2013 Dec 26;61(51):12646-52. doi: 10.1021/jf404726z. Epub 2013 Dec 17.
- Niu Y et al.; Characterization of a novel alkali-soluble heteropolysaccharide from tetraploid Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino and its potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties; Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry; 2014 Apr 30;62(17):3783-90. doi: 10.1021/jf500438s. Epub 2014 Apr 18.
- Yang F, Shi H, Zhang X, Yang H, Zhou Q, Yu LL; Two new saponins from tetraploid jiaogulan (Gynostemma pentaphyllum), and their anti-inflammatory and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities; Food Chemistry; 2013 Dec 15;141(4):3606-13. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.06.015. Epub 2013 Jun 13.
- Tom Hsun-Wei Huang, Yuhao Li, Valentina Razmovski-Naumovski, Van Hoan Tran, George Qian Li, Colin C. Duke, Basil D. Roufogalis; Gypenoside XLIX isolated from Gynostemma pentaphyllum inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB activation via a PPAR-alpha-dependent pathway; Journal of Biomedical Science; July 2006, Volume 13, Issue 4, pp 535-548
- Zhang C, Yang X, Xu L; Immunomodulatory action of the total saponin of Gynostemma pentaphylla; Chinese Journal of Modern Developments in Traditional Medicine; [1990, 10(2):96-8, 69-70]
- FU Yi, The Experimental Study for Gynostemma pentaphyllum With Sport Endurance; Journal Of Chehgdu Physical Education Institute; 2000-02
- LI Yan-ru; Efects of Gynostemma pentaphllum Polysaccharides on Immuning Ability of Exercise Fatigue Mice; Food Science; 2008-08
- Huang WC, Kuo ML, Li ML, Yang RC, Liou CJ, Shen JJ; Extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum enhanced the production of antibodies and cytokines in mice; Yakugaku Zasshi; 2007 May;127(5):889-96.
- ZHOU Li, YE Kai-he, REN Xian-da; Effects of gypenosides to the immune deficit mouse’s non-specific immunological function; Chinese Journal of Primary Medicine and Pharmacy; 2006-06
- ZHANG Yong-Xiang et al.; Effects of gypenosides on splenocyte proliferation and relationships with hypothalamic and splenic norepinephrine and plasma corticosterone in rats; Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology; 1992-04.
- QIAN Bo-chu et al.; Influence of gypenosides on immunological function in rodents; Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology; 1986-01
- Li Lin, Xing Shantian; Effects of gypensides on lymphocyte proliferation and interleukin-2 production in spleen of mice; Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica; 1992-01
- Bin Xiaonong, Tan Min; Effect of Gypenosides on Natural Killer Cells Activity of Spleen in Mice; Journal Of Hengyang Medical College; 1994-02
- LIU Yu-ping,YU Miao,LI Lin,YIN Xiang-min; Studies of Gypenosides on Antitussive-expectorant and Immunoenhancement Effects; Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 2009-05
- SHEN Hong-chun; Effects of Gyrtostemma on Antioxidant Capacity and Immune Functions in Weaning Piglets; Journal of Hubei University for Nationalities(Natural Science Edition); 2012-01
- Zhang Chongquan, Yang Xiaohui, Xu Linben; Study on the Immunomodulatory Action of the Total Saponin of Gynostemma pentaphylla; Hunan Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica; 1990-02
- GE Sheng, JIANG Xiao-wen, WANG Zhi-xin, YU Wen-hui; Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb) Makino on immune function in chickens; Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine; 2010-03
- Wang Bin,Ge Zhidong,Zhou Aiwu et al.; Effects of Gypenosides on Immune Function of Rats in Vitro; Traditional Chinese Drug Research & Clinical Pharmacology; 1999-01
- LIU Yu-ping, YU Miao, YIN Xiang-min; Observation of gypenosides to the mouse respiratory inflammation and immunoenhancement effect; Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy; 2009-13
- Hopper, RA; Garthwaite, J (2006). “Tonic and phasic Nitric Oxide signals in hippocampal long-term potentiation.“. Journal of Neuroscience 26 (45): 11513–21.doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2259-06.2006. PMID 17093072.
- Taqatqeh, F; Mergia, E; Neitz, A; Eysel, UT; Koesling, D; Mittmann, T (2009). “More than a retrograde messenger: Nitric Oxide needs two cGMP pathways to induce hippocampal long-term potentiation.”. Journal of Neuroscience 29 (29): 9344–50
- Yun HY, Dawson VL, Dawson TM; Nitric oxide in health and disease of the nervous system; Molecular Psychiatry. 1997 Jul;2(4):300-10.
- Calabrese V, Mancuso C, Calvani M, Rizzarelli E, Butterfield DA, Stella AM; Nitric oxide in the central nervous system: neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity; Nature Reviews. Neuroscience; 2007 Oct;8(10):766-75.
- Olivia May, Ph.D.; Nitric Oxide Contribution in the CNS: a NO brainer; Cayman Chemical; 2015.
- Gilgun-Sherki Y, Melamed E, Offen D; Antioxidant treatment in Alzheimer’s disease: current state; Journal of Molecular Neuroscience; 2003;21(1):1-11.
- Ebadi M, Srinivasan SK, Baxi MD; Oxidative stress and antioxidant therapy in Parkinson’s disease; Progress in Neurobiology; 1996 Jan;48(1):1-19.
- Meng X et al.; Attenuation of Aβ25-35-induced parallel autophagic and apoptotic cell death by gypenoside XVII through the estrogen receptor-dependent activation of Nrf2/ARE pathways; Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology; 2014 Aug 15;279(1):63-75. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.03.026. Epub 2014 Apr 12.
- ZHOU Wei-Hua, TAN Li-Ming, MI Chang-Zhong et al.; Effects of gypenosides on the hippocampal cholinergic system in D-galactose induced Alzheimer’s disease in mice; Chinese Journal of Gerontology; 2012-22
- Deng Jiagang,Du Zhengcai,Hao Erwei; Effect of Compound Jiao Gu Lan Medicines on Memory and Brain Monoamine Oxidase Activity of Mice; World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine; 2007-12
- Jianjun Gao, Yoshinori Inagaki, Xuan Li, Norihiro Kokudo, Wei Tang; Research progress on natural products from traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease; Drug Discoveries & Therapeutics. 2013; 7(2):46-57; DOI: 10.5582/ddt.2013.v7.2.46
- Keon Sung Shin et al.; Gypenosides attenuate the development of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat model of Parkinson’s disease; BMC Neuroscience 2015, 16:23; doi:10.1186/s12868-015-0163-5
- Burnett AL; The role of nitric oxide in erectile dysfunction: implications for medical therapy; Journal of Clinical Hypertension (Greenwich); 2006 Dec;8(12 Suppl 4):53-62.
- Deng Q, Yang X; Protective effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum polysaccharides on PC12 cells impaired by MPP(+); International Journal of Biolological Macromolecules; 2014 Aug;69:171-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.05.049. Epub 2014 May 26.
- Shin KS, Zhao TT, Choi HS, Hwang BY, Lee CK, Lee MK; Effects of gypenosides on anxiety disorders in MPTP-lesioned mouse model of Parkinson’s disease; Brain Research; 2014 Jun 3;1567:57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.04.015. Epub 2014 Apr 18.
- Choi, H.S.; Park, M.S.; Kim, S.H.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, C.K.; Lee, M.K. Neuroprotective Effects of Herbal Ethanol Extracts from Gynostemma pentaphyllum in the 6-Hydroxydopamine-Lesioned Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules 2010, 15, 2814-2824.
- Li K, Du Y, Fan Q, Tang CY, He JF; Gypenosides might have neuroprotective and immunomodulatory effects on optic neuritis; Medical Hypotheses. 2014 May;82(5):636-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2014.02.030. Epub 2014 Mar 6.
- Zhou Yili; Effects Of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum ( Thunb ) Makino Hypomnesis Of The Aged And The Visual Evoked Potential; Journal of Wenzhou Medical College; 1991-01
- ZHANG Xiao-yu,LI Yan,YONG Bin,LIU Jian-ting,YAN Wei; Study on Gynosaponins Compound on Ameliorating Memory in Mice; Food Science; 2007-03
- Hong SW, Yang JH, Joh EH, Kim HJ, Kim DH; Gypenoside TN-2 ameliorates scopolamine-induced learning deficit in mice; Journal of Ethnopharmacology; 2011 Apr 12;134(3):1010-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.02.002. Epub 2011 Feb 17.
- Chang Shuying, Kuang Peigen et al.; Memory Facilitation Induced By Gynostemma Pentaphyllum And Gypenoside 3 (GINSENOSIDER B_1) In Mice; Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin; 1988-06
- Dong L et al. Gypenosides protected the neural stem cells in the subventricular zone of neonatal rats that were prenatally exposed to ethanol; International Journal of Molecular Sciences; 2014 Nov 28;15(12):21967-79. doi: 10.3390/ijms151221967.
- Qi G, Zhang L, Xie WL, Chen XY, Li JS; Protective effect of gypenosides on DNA and RNA of rat neurons in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury; Acta Pharmacologica Sinica; 2000 Dec;21(12):1193-6.
- Schild L, Cotte T, Keilhoff G, Brodemann R; Preconditioning of brain slices against hypoxia induced injury by a Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract–stimulation of anti-oxidative enzyme expression; Phytomedicine. 2012 Jun 15;19(8-9):812-8. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.03.012. Epub 2012 Apr 17.
- Schild L, Cotte T, Keilhoff G, Brodemann R; Protection of hippocampal slices against hypoxia/hypoglycemia injury by a Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract; Phytomedicine. 2009 Aug;16(8):734-43. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2009.03.006. Epub 2009 Apr 29.
- Chen Qianfen, Tian Hecun, Zhang Chenyin, Chu Dekai, Yang Weidong; Protective effect of gypenosides on global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat; Acta Academiae Medicinae Bengbu; 1996-06
- Chi Mingyu et al.; Protection Of Jiaogulandan On The Mouse Brain Withfocal Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury; Guangxi Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 2003-04
- TANG Xiao-qing, ZHU Bing-yang, CHEN Jian-xiong et al.; Protective Effect of Gypenosides on Ischemic Brain Damage Induced by Photochemistry; Journal of Hengyang Medical College; 2001-02
- ZHANG Xiu-mei, CAO Xiao-qing, WEI Xin-bing et al.; Antioxidant effects of gypenosides on focal brain ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats; Acta Academiae Medicinae Shandong. 2002-01
- Qi minfang,Luo chanlan,Qin wei,Tian hong,Chen yuanshou; Gynostemma improves vascular dementia-induced cognitive dysfunction in mice; Acta Academiae Medicinae Zunyi; 2012-05
- WANG Zhu-Yun, QIU Pei-Lun; Protective effect of gypenosides on acute incomplete cerebralischemia in rabbits; Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology; 1992-03
- Yan Jiongjiong, Yue Wenhao, Han Danchun et al.; Effects of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum on Cognitive Functions of Cerebral Infarct Patients; Chinese Journal Of Clinical Psychology; 1997-02
- Yang Jiongjiong, Yue Wenhao, Han Danchun et al.; Study of PRVEP about effects of gynostemma pentaphyllum on brain dysfunction of patients after brain infarction; Chinese Journal of Behavioral Medical Science; 1998-04
- WANG Xu-ping et al.; Protection of gypenoside on glutamate-induced oxidation in the cultured cortical neurons of embryonic rats; Journal of Shandong University(Health Sciences); 2006-06
- LIU Lu-hua et al.; Protective effect of gypenosides-containing serum against oxidation neurotoxicity induced by glutamate; Journal of Shandong University(Health Sciences); 2008-04
- HAN Yu-xia, WEI Xin-bing, LI Xia, DING Yan, XIN Hua, DING Hua; Protective effects of gypenosides against glutamate-induced hippocampus injury in rats; Journal of Shandong University(Health Sciences); 2008-05
- XIN Hua, SHANG Lin-shan, LIU Jin-Cheng, et al.; Protective effects of gypenoside against oxidative neurotoxicity induced by glutamate; Journal of Shandong Univenity(Health Scicnes); 2004-06
- Zhang, Yi-Qun et al. Immediate effects of a gypenosides-containing tonic on the echocardiography of healthy persons of various ages. Journal of Guiyang Medical College 1993 18(4):261.
- Zhou, Ying-Na et al. Influence of kiwifruit/jiaogulan recipe on the lung function and exercise endurance under exercise workload. Journal of Guiyang Medical College (Chinese) 1993;
- Fisker S et al.; The role of nitric oxide in L-arginine-stimulated growth hormone release; Journal of Endocrinolical Investigation; 1999;22(5 Suppl):89-93.
- Zhou, Ying-Na et al. Effects of a gypenosides-containing tonic on the pulmonary function in exercise workload. Journal of Guiyang Medical College 1993 18 (4):261.
- Chen, LF et al. Comparison between the effects of gypenosides and gensenosides on cardiac function and hemodynamics in dogs. Zhongguo Yaolixue Yu Dulixue Zazhi 1990; 4(1): 17-20. )
- Yong-jiang Ding et al.; Effects of Gypenosides from Gynostemma pentaphyllum supplementation on exercise-induced fatigue in mice; African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 5(8), pp. 707-711, 18 April, 2010; DOI: 10.5897/AJAR10.002
- Long Bibo, Zhang Kun, Hu Jinxiang, Zhou Zhongkai, Zhou Xuelan; The effect of gynostemma pentaphyllum(GP) on the activities of CK,LDH and LG,MG of mice; Journal of Hainan Normal University(Natural Science); 2008-0
- B. Qi, H. Huang, “Anti-Fatigue Effects of Polysaccharides from Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino by Forced Swimming Test“, Advanced Materials Research, Vols. 881-883, pp. 426-429, Jan. 2014
- C. J. Li, A. Li, “The Effects of Polysaccharide fromGynostemma pentaphyllum Supplementation on Exhaustive Exercise-Induced Fatigue“, Applied Mechanics and Materials, Vol. 730, pp. 241-244, Jan. 2015
- Xingsheng Chen; Research of Thelenota Ananas Sports Drinks Action to Race Walking Athletes; Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology 7(6): 395-397, 2015
- Bin Xiao-Nong et al.; Effect of Gypenosides on Malondialdehyde Content and Superoxide Dismutase Activity of Cardiac and Renal Tissue in Exhaustive Mice; Journal Of Hengyang Medical College; 1994-01
- Lin-Na S, Yong-Xiu S; Effects of polysaccharides from Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.), Makino on physical fatigue; AJTCAM; 2014 Apr 3;11(3):112-7. eCollection 2014.
- LI Ya-jing et al.; Effect of Complex Liquid of Gynostemma pentaphllum on Fatigue Resistance of Mice; Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences; 2009-29
- Long Bibo,Zhang Xindin,Shu Jiawen; Effect of Gvnoslemma penlaphllum on training rat liver’s free radical metabolism and serum enzymein; Journal of Hainan Normal University(Natural Science); 2008-02
- LONG BI-bo; Experimental Research On The Anti-Fatigue Effect Of Extraction Of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum; Modern Preventive Medicine; 2009-04
- Yao Shishuo, et al.; Composition and Anti-Fatigue Mechanism of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Produced in Mountain Areas in South Anhui of China; China Sport Science; 1991-05
- Chi A, Tang L, Zhang J, Zhang K; Chemical Composition of Three Polysaccharides From Gynostemma pentaphyllum and Their Antioxidant Activity in Skeletal Muscle of Exercised Mice; International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism; 2012 Dec;22(6):479-85.
- Choi, H.S. et al.; Ameliorating Effects of Herbal Ethanol Extract from Gynostemma pentaphyllum on Chronic Stress-Induced Anxiety in Mice; AGRIS Volume: 42, Issue: 1; 2013
- Choi, H.S. et al.; Anxiolytic Effects of Herbal Ethanol Extract from Gynostemma pentaphyllum in Mice after Exposure to Chronic Stress; Molecules 2013, 18(4), 4342-4356; doi:10.3390/molecules18044342
- TT Zhao, KS Shin, HS Choi, HJ Park, MK Lee; Effects of gypenosides on chronic stress-induced anxiety in mice; Planta Medica 2014; 80 – P1C8; DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1394633
- Gao Ying-dong, Chen Wu, Xiong Xiao-juan, Li Kai-quan, Zou Sheng-qin; Effects of Gypenosides on the stress ability of rats; Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation; 2005-43
- Seong-Hae Jeong, Myung Koo Lee, Mi Sook Park, Jae-Moon Kim; Randomized, Double-Blind Study of Efficacy and Safety of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Ethanol Extract in a Normal Population; Korean Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, Vol. 21, No. 2. 2011
- WANG Jun-ming, WANG Shuai, CUI Ying; Antidepressant Activities of Extracts from Gynostemma pentaphyllum(Thunb.) Makino; Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research; 2012-04
- Rehman Gauhar et al.; Heat-processed Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract improves obesity in ob /ob mice by activating AMP-activated protein kinase; Biotechnology Letters; September 2012, Volume 34, Issue 9, pp 1607-1616
- Phi Hung Nguyen et al.; New dammarane-type glucosides as potential activators of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) from Gynostemma pentaphyllum; Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry; Volume 19, Issue 21, 1 November 2011, Pages 6254–6260
- B Perry, Y Wang; Appetite regulation and weight control: the role of gut hormones; Nutrition and Diabetes (2012) 2, e26; doi:10.1038/nutd.2011.21
- Soo-Hyun Park et al.; Antiobesity effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract (actiponin): A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial; Obesity, Volume 22, Issue 1, pages 63–71, January 2014; DOI: 10.1002/oby.20539
- Chou SC et al.; The add-on effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine; 2006 May-Jun;12(3):34-9.
- Chen Daiyi, Chen Huizhen, Su Jingde, Song Yuxia, Zhang Yingliang; Analysis of Curative Effect for Hepatitis B Carrier by Compound Jiaogulan Liquid; The No 421 Central Hospital of Guangzhou Navy; 1995-10
- Zhu, BZ; Therapeutic effect of jiaogulan granules on 100 patients with chronic hepatitis B; Journal of Anhui College of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Chinese. 1994; 13(3): 7.
- Ma, YL et al.; Therapeutic effect of jiaogulan in 200 cases of hepatitis B; Hebei Journal of combined Chinese and Western Medicine. Chinese, 1997; 6(1):
- Chen MH et al.; The molecular mechanism of gypenosides-induced G1 growth arrest of rat hepatic stellate cells; Journal of Ethnopharmacology; 2008 May 8;117(2):309-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2008.02.009. Epub 2008 Feb 14.
- Chen MH et al.; The inhibitory effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum on MCP-1 and type I procollagen expression in rat hepatic stellate cells; Journal of Ethnopharmacology; 2009 Oct 29;126(1):42-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.08.012. Epub 2009 Aug 21.
- Tao Jianwu, Yao Caiping, Wang Jichun, Hao Guangli, Ye Zhengjun; Inhibitory effects of gynostemma pentaphyllum on lipid peroxidation reaction in rats liver; Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacy; 2001-03
- Lin Liu et al.; The Effect of Gypenosides on TGF-β1/Smad Pathway in Liver Fibrosis Induced by Carbon Tetrachloride in Rats; International Journal of Integrative Medicine, 2013, Vol. 1, 23:2013
- Jung-Chou Chen et al.; Therapeutic Effect of Gypenoside on Chronic Liver Injury and Fibrosis Induced by CCl4 in Rats; The American Journal of Chinese Medicine; 28, 175 (2000). DOI: 10.1142/S0192415X00000222
- Xu Shenglin; A Comparison on the Protecetive Action Against Liver Lesions of Total Saponins of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum and Oleanolic Acid; Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy; 1989-03
- LUO Wen-zheng, ZHANG Qing-zhong, LV Zhi-ping; The Application of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Makino in Fatty Liver Disease Treatment; Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 2009-08
- Qin R. et al.; Protective effects of gypenosides against fatty liver disease induced by high fat and cholesterol diet and alcohol in rats; Archives of Pharmaceutical Research; 2012 Jul;35(7):1241-50. doi: 10.1007/s12272-012-0715-5. Epub 2012 Aug 3.
- Zhao J. et al.; Gypenoside attenuates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice via anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic bioactivities; Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine; 2014 May;7(5):1388-1392. Epub 2014 Feb 21.
- ZHANG Yong,XIAO HouQin,ZHANG JieE,et al.; The protective and therapeutic effects of Gypenosides in patients with early stage chronic renal failure; Journal of Clinical Internal Medicine; 2007-10
- Sun Wansen,Wu Xili,Qiao Chenglin; Clinical Study of Gypenodide on Therapeutic Chronic Renal Failure; Journal of Zhejiang College of TCM; 2004-02
- Xia Chengyun, Liou Xiaohui, Deng Longyin; Effects Of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Makion On Endothelin In Plasma, Blood Lipids And Function Of Patients With Chronic Renal Insufficiency; China Journal Of Modern Medicine; 2000-1
- Hesse C, Razmovski-Naumovski V, Duke CC, Davies NM, Roufogalis BD; Phytopreventative effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum against acute Indomethacin-induced gastrointestinal and renal toxicity in rats; Phytotherapy Research; 2007 Jun;21(6):523-30.
- Zhang Y, Zhang JE, Xiao HQ, Wu PY, Bai SJ; Gypenosides inhibit renal fibrosis by regulating expression of related genes in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction; Journal of Nephrology; 2011 Jan-Feb;24(1):112-8.
- ZHANG Yong, DING Guohua, ZHANG Jiane,et al.; Effect of Gypenosides on Expression of Connective Tissue Growth Factor(CTGF) in UUO Rats with Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis; Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Nephrology; 2005-07
- LI Hongqin, YANG Jingmei, GAO Shan, ZHAO Min, HU Jiying; Effects of Gynostemma on Transient Hyperuricemia in Mice; Journal of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine; 2010-01
- Chian-Jiun Liou et al.; Long-term oral administration of Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract attenuates airway inflammation and Th2 cell activities in ovalbumin-sensitized mice; Food and Chemical Toxicology; Volume 48, Issue 10, October 2010, Pages 2592–2598; doi:10.1016/j.fct.2010.06.020
- Wen-Chung Huang et al.; Gynostemma pentaphyllum Decreases Allergic Reactions in a Murine Asthmatic Model; The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, Volume 36, 579 (2008). DOI: 10.1142/S0192415X08005990
- Hunan Journal of Chinese Medicine 1993;9(4):11.
- Qu, Jing et al. “Study of the therapeutic effects of Chinese herb, jiaogulan in 537 cases of chronic tracheo-bronchitis.”; Bulletin of Chinese Herbs and Medicines. Chinese. 1972. (2): 24.
- Liu, ZX; Therapeutic effect of jiaogulan on 86 patients with chronic bronchitis; Hunan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Chinese. 1993; 9(4): 11.
- Hu, BC, et al. Therapeutic effect of gypenosides in 96 cases of chronic bronchitis. Research on Chinese Herbs. Chinese, 1996; 4, 136.
- Rujjanawate C, Kanjanapothi D, Amornlerdpison D; The anti-gastric ulcer effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino; Phytomedicine. 2004 Jul;11(5):431-5.
- Journal of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine 1991;11(12):713.
- Chen L, Tai WCS, Brar MS, Leung FCC, Hsiao WLW (2015); Tumor Grafting Induces Changes of Gut Microbiota in Athymic Nude Mice in the Presence and Absence of Medicinal Gynostemma Saponins. PLoS ONE 10(5): e0126807. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0126807
- Achike, F. I. and Kwan, C.-Y. (2003); Nitric oxide, human diseases and the herbal products that affect the nitric oxide signalling pathway; Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, 30: 605–615. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2003.03885.x
- Toda N, Ayajiki K, Okamura T; Nitric oxide and penile erectile function; Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2005 May;106(2):233-66. Epub 2005 Mar 2.
- Marinella Rosselli, Paul J.Keller, Raghvendra K.Dubey; Role of nitric oxide in the biology, physiology and pathophysiology of reproduction; Human Reproduction Update 1998, Vol. 4, No. 1 pp. 3–24
- TAN Hua-bing, HE Qin; Influence of the High lipemia and Fiveleaf Gynostemma Herb on the Microstructure of Testicle of the Adult Male Rabbit; Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine; 2008-07
- MA Shan feng, LU Zong lan, GUAN Su dong, LIU Gui lan; Antagonistic effect of gypenoside on diaphragm against doxorubicin cytotoxicity; Journal Of Bengbu Medicinae College; 2000-05
- Lei Jianhua et al; Preventive Effect of Gypenoside Against Endotoxic Shock-Induced DIC in rabbit; Journal Of Hengyang Medical College; 1994-02
- Sumitra Suntararuks et al.; Immunomodulatory Effects of Cadmium and Gynostemma pentaphyllum Herbal Tea on Rat Splenocyte Proliferation; Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2008, 56 (19), pp 9305–9311; DOI: 10.1021/jf801062z
- Liu, Jialiu. “Overall health-strengthening effects of a gypenosides-containing tonic in middle aged and aged persons.” Journal of Guiyang Medical College 3 (1993): 146.
- Gopinathan Menon, Sujatha Dokka, Brian Jones; Topical cosmetic composition having a natural plant active ingredient and method of using same; US Patent/Publication number US20050147578 A1; Jul 7, 2005.
- DENG Dan-qi, WANG Yi-lin, YUAN Li-mei, HU Rong, LIU Liu; The Effects of Gypenosides(GP) on Protein Expression of IκB and IKK in the Signaling Pathway of Nuclear Factor Kappa B in Photo-damaged Skin of Balb/C Mice; Journal of Kunming Medical University; 2010-02
- Stansbury, Jill; Saunders, Paul; Winston, David; Supporting Adrenal Function with Adaptogenic Herbs; Journal of Restorative Medicine, Volume 1, Number 1, September 2012, pp. 76-82(7); DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.14200/jrm.2012.1.1007
- Li XL et al; Purification of a polysaccharide from Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino and its therapeutic advantages for psoriasis; Carbohydrate Polymers. 2012 Aug 1;89(4):1232-7. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.04.001. Epub 2012 Apr 7.
- Okoye, EL; Ezeifeka, GO and Esimone, CO. The antiviral activity of ‘Gynostemma pentaphyllum’ against yellow fever virus. Australian Journal of Herbal Medicine, Vol. 24, No. 4, 2012: 128-134.
- Okoye, E. L; In vitro evaluation of the antiviral activity of extracts of Gynostemma pentaphyllum against poliomyelitis virus; International Journal of Agriculture and Biosciences 2013 Vol. 2 No. 2 pp. 64-67
- EL Okoye, CS Nworu, GO Ezeifeka, CO Esimone; Inhibition of HIV-1 lentiviral particles infectivity by Gynostemma pentaphyllum extracts in a viral vectorbased assay; African Journal of Biotechnology, Vol 11, No 7 (2012)
- Darunee Srichana, Rattana Taengtip, Sumalee Kondo; Antimicrobial Activity Of Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Extracts Against Fungi Producing Aflatoxin And Fumonisin And Bacteria Causing Diarrheal Disease; Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, Vol 42 No. 3 May 2011 p. 704-710.
- Chinese Journal of Practical Internal Medicine 1993;13(12):725.
- Attawish A. et al; Chronic toxicity of Gynostemma pentaphyllum; Fitoterapia. 2004 Sep;75(6):539-51.
- Chiranthanut N. et al; Toxicity evaluation of standardized extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino; Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2013 Aug 26;149(1):228-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.027. Epub 2013 Jun 21.
- Chen J, et al; Antistress action of Gynostemma pentaphyllum; Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine. 1989; 11(1):31–32.
- Li R, et al; Chemical and pharmacological studies on Gynostemma pentaphyllum; Journal of New Chinese Medicine. 1988; 20(4):51–53.
- Null, G PHD. (2011); Death by Medicine. Mount Jackson, VA: Praktikos Books.